Modern mathematical methods and approaches to solving various applied problems in frames of the general decision making theory are considered. The decision making theory deals with the process of optimal alternative selection from a set of possible alternatives and corresponding models. Exposition includes types of conditions for making the decision: full information condition (criteria analysis), risk or uncertainty condition (game theory) and partial information condition (statistical games or games against Nature). Analysis and solution examples in business-related tactical and strategic problems are presented. Major attention is devoted to the ways of formalization, modeling and interpretation of analysis results and solutions. In particular, the poser of method’s adaptability and its restrictions are discussed. Textbook is designed for students of economic, marketing, management departments and for everyone who is interested
O. Y. Uritskaya. Decision-Making Theory: Lecture Textbook // St.Petersburg: SPbSTU Press, 1999.
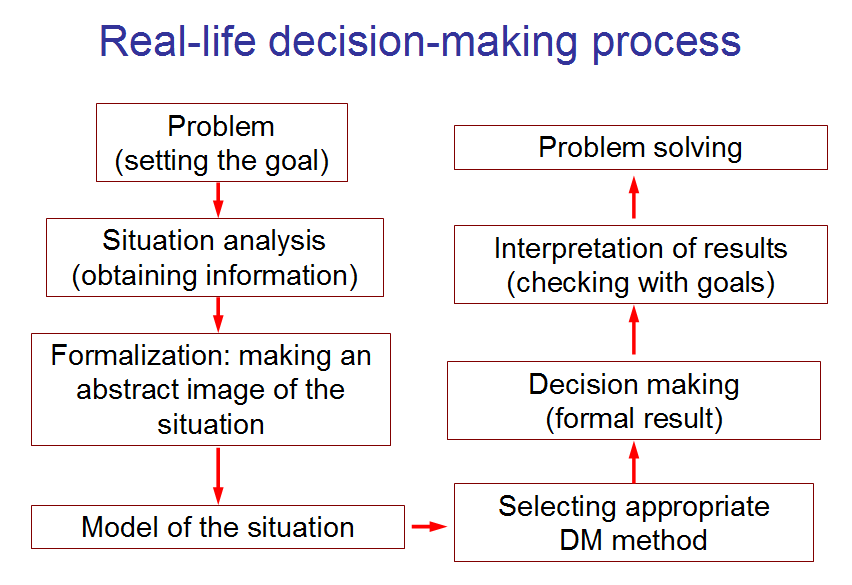
Fig. 1. Decision-making (DM) as a process is much longer than we use to believe.
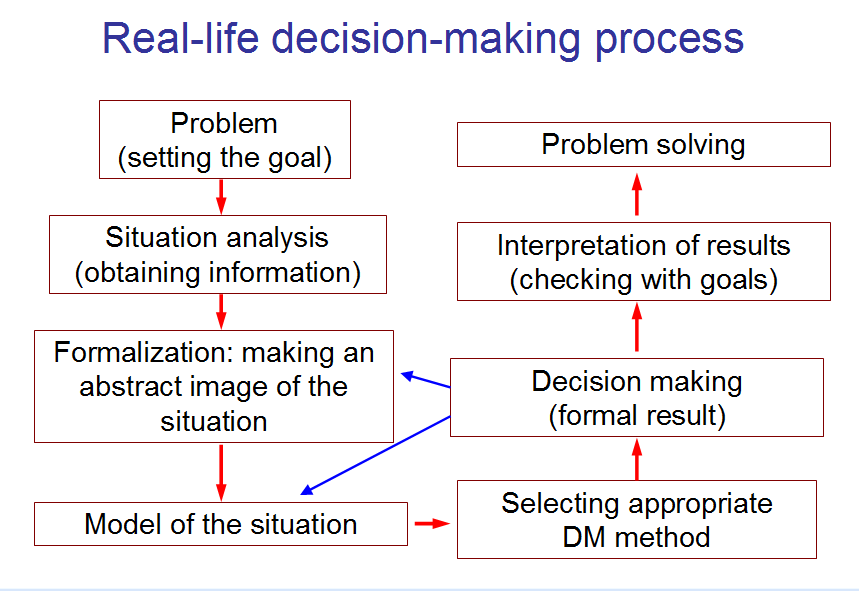
Fig. 2. Decision-making results refer not to the initial problem, but to formalized model of situation, which was built using only information available at the moment.
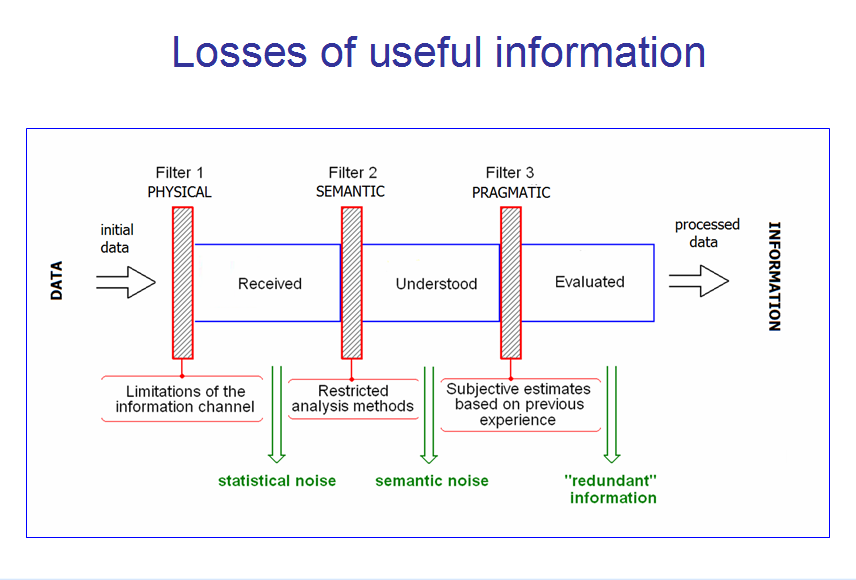
Fig. 3. Sensitivity to information. Process transformation of data to the information. Preceding throw the physical, semantic and pragmatic filters significant part of important information can be lost with statistical and semantic noise or is not recognized as useful one.
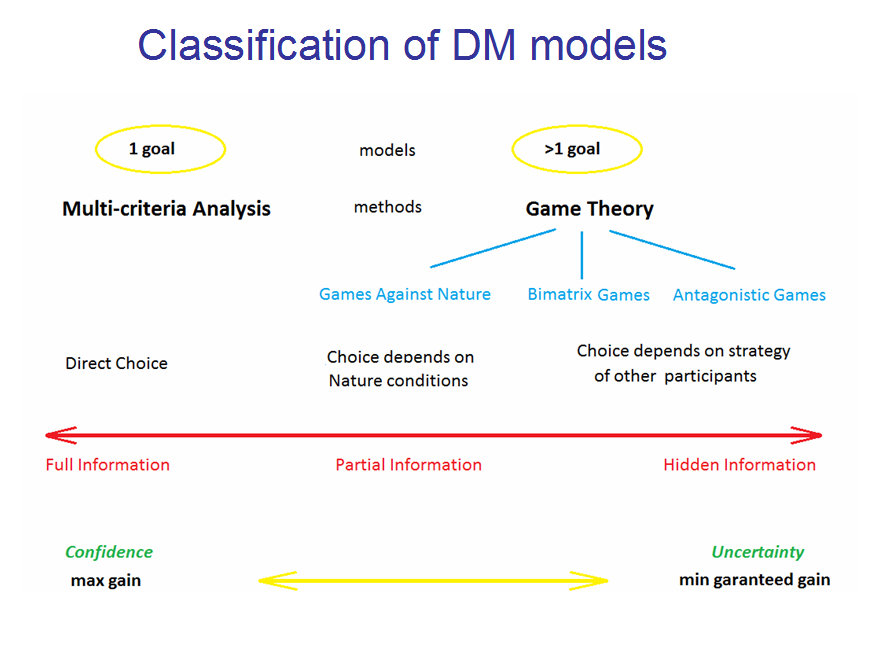
Fig. 4. Classification of DM models. Choosing wrong model of situation leads to the critically wrong results.